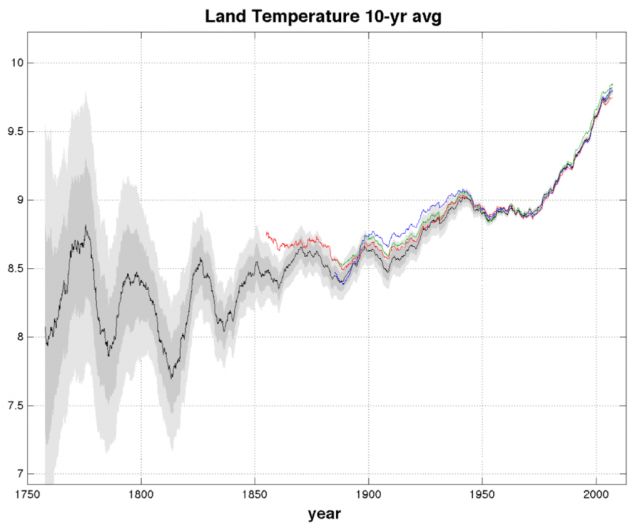
Enlarge / The gray areas are one and two standard deviations from the calculated temperature (black line). The other surface temperature records are colored red, green, and blue.
Berkeley Earth
Despite plenty of indications that the Earth has gotten warmer—like melting glaciers and ecosystems that are shifting toward the poles—there are a number of climate skeptics who simply don't accept the temperature records produced by three different organizations (NASA, NOAA, and the CRU). Many of them pinned their hopes on physicist Richard Muller, who was also not convinced the professionals had gotten it right. But Muller did something about it, forming the Berkeley Earth project, and building a huge database of land temperature records.
Back in October, Muller dropped his findings in a rather unconventional location: an editorial in The Wall Street Journal. Despite the hype, the results were rather bland. He produced a temperature record that was nearly identical to that of the other organizations. But now, Muller is back for round two, and this time he has chosen the New York Times as an outlet for his climate musings.
As before, his team uses a different statistical method of reconstructing temperatures that works well with short records, taken at sites that were shut or moved. NASA, NOAA, and the CRU use methods that require long records, so they have to make adjustments to the data from sites that have shifted or gotten new equipment. This compensates for the fact that these changes will lead to discontinuities in the record. Since Berkeley Earth doesn't need the same length, it can just skip adjustments entirely: any record with a discontinuity is just split there, and treated as two records. The team has now also pushed its analysis back to almost 1750, adding a century to the land temperature records produced elsewhere.
Read 7 remaining paragraphs | Comments
DIGITAL JUICE
No comments:
Post a Comment
Thank's!